

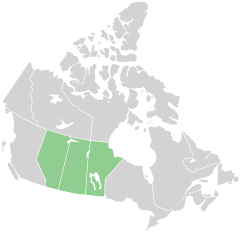
Prairies have similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. The Canadian Prairies occupy vast areas of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta.
Main climates: The climate of the Canadian prairie region is defined as semi arid (partly dry), snowy, fully humid with cool summers, fully humid with warm summers, semi-cold and arid climate.
Precipitation (rain & snow) in the Canadian prairies are very important to study as these locations make up 80% of the country's agricultural(farming) production. Saskatchewan obtains the least amount of precipitation annually and Manitoba receiving the most. Most rainfall typically happens in the summer months such as June and July. With the high humidity of the prairies, tornadoes are likely to occur due to the relatively flat surface of the region.
Population:
| Rank |
Census metropolitan area |
Population (2011) |
Population (2006) |
Province |
| 1 |
Calgary |
1,214,839 |
1,079,310 |
Alberta |
| 2 |
Edmonton |
1,159,869 |
1,034,945 |
Alberta |
| 3 |
Winnipeg |
730,018 |
694,668 |
Manitoba |
| 4 |
Saskatoon |
260,600 |
233,923 |
Saskatchewan |
| 5 |
Regina |
210,556 |
194,971 |
Saskatchewan |
Growth: Some of the prairie region of Canada has seen rapid growth from a boom in oil . The prairie provinces had grown by 14.6% to 6,748,280.
Culture and politics: The Prairies are distinguished from the rest of Canada by cultural and political traits. The oldest influence on Prairie culture are the First Nations, who have lived in the area for millennia. The first Europeans to see the Prairies were fur traders and explorers from eastern Canada (mainly present-day Quebec) and Great Britain via Hudson Bay. They gave rise to the Métis, working class "children of the fur trade."[5] During their settlement by Europeans, the prairies were settled in distinct ethnic block settlements giving certain areas distinctively Ukrainian, German, French, or Scandinavian Canadian cultures.
Economy/resources:
Between 1670 and 1870, the Hudson’s Bay Company was granted exclusive fur trading rights to the area drained by the rivers flowing into Hudson Bay, then called Rupert's Land.
 bison
bison
The earliest significant human modification of the native prairie ecosystems was spurred by European demand for products of the fur trade, particularly those from bison. The killing of thousands of bison each year by European settlers led to the virtual elimination of free-roaming bison by the 1880s.
 Hudson's Bay Area
Hudson's Bay Area
Railways played a leading role in defining the pattern of development. Towns emerged along the rail line as collection points for grain and livestock exports and as distribution points for incoming supplies. By 1916, Canada was leading the world in wheat exports. Twenty-five years later, 60% of the Prairies Ecozone was under cultivation and the landscape resembled a checkerboard.
In 1936, farmers represented 50% of the population. Today that number has fallen to less than 10%. Population decline in the rural areas and growth in the urban areas has been the general rule since the 1950s. Although urban use of land is tiny in terms of area (0.3%), it remains an important influence on the ecozone. Today, the proportion of the urban population is 81% compared with 76% for all of Canada, a remarkable figure given that agricultural activities dominate the landscape of this ecozone. In 1991, the total population of the Prairies Ecozone was approximately 3.8 million, an increase of 25% since 1971. The major population centres are Calgary, Edmonton, Saskatoon, Regina and Winnipeg.
The economy of the prairies include industries of agriculture, mining, and gas and oil. The Prairies provide 19% of Canada's total resource-based employment, with agricultural activities and food processing accounting for nearly 62% of the total. Its minerals industry (fossil fuels and related products) accounts for nearly a third of Canada's total employment in this sector.
The Prairies farm a variety of crops such as grain, canola, beef, dairy, pigs, horses, chickens, and turkeys.
Mining is the second most important industry. In Saskatchewan, mines include potash, uranium, coal, gold, salt, meta-kaolin, silica sand, sodium sulphate, clay and bentonite. In Alberta, mines include oil sands; coal; limestone; salt; shale; dimension stone; ammonite shell; sandstone; sand and gravel. Land use for oil production has declined over the past decade.
The Prairie economy is now shifting toward service-based sectors such as processing food, wood, metals, chemicals, and petrochemicals which are chemical made from petroleum and natural gas. Petroleum is a liquid mixture of hydrocarbons that is present in certain rock strata and can be extracted and refined to produce fuels including gasoline, kerosene, and diesel oil.
Videos:
What is a Prairie
Prairie Tall Grass
History of the Canadian Prairies
Beauty of the Prairies
Sources:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canadian_Prairies
https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/environment/resources/publications/impacts-adaptation/reports/assessments/2008/ch7/10381
http://ecozones.ca/english/zone/Prairies/human.html
Websites:
https://thecanadaguide.com/places/the-prairies/
https://www.roughguides.com/destinations/north-america/canada/prairie-provinces/
https://www.britannica.com/place/Prairie-Provinces
https://www.arcgis.com/apps/MapJournal/index.html?appid=03401e1560e14ffea990099d89852d90
https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/environment/resources/publications/impacts-adaptation/reports/assessments/2008/ch7/10381
http://ecozones.ca/english/zone/Prairies/human.html











 bison
bison  Hudson's Bay Area
Hudson's Bay Area